背景: 使用 websocket 来发送语音chunk并使用 faster-whisper 来进行语音识别。
客户想知道单台服务器的并发量有多大,有哪些具体的指标。
记录一下我简单的测试,工具使用
环境
本人实验在 Azure gpu 虚拟机上进行
虚拟机的型号为 Standard_NC4as_T4_v3
具体的硬件设施为:
- 4 vcpu
- 28 GiB RAM
- NVIDIA T4
- 16G
- 128G SSD
tesla t4 是一张比较老的推理卡,显存比较大,但是core核心数比较少,推理速度不算太快
cuda环境
- 安装 nv-gpu驱动
- 安装 cudatoolkit
- 安装 cudann
可以看这个:
linux-deeplearn-env | Akabane71
python环境
uv venv .venv -p 3.11
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install fastapi[all] soundfile faster-whisper uvicorn pip websocket-client locust
server 端
import os
import asyncio
import itertools
import time
from typing import BinaryIO
import io
import uvicorn
from starlette.websockets import WebSocketDisconnect
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse,JSONResponse
from faster_whisper import WhisperModel
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket,Request
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
from numpy import info
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
TMP_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "tmp")
SOUNDS_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "sounds")
app = FastAPI()
# 设置CORS中间件
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
model_size = "large-v3" # "large-v3" or "large-v2" or "large-v3-turbo"
# 创建n个模型实例
model_pool = [
WhisperModel(model_size, device="cuda", compute_type="int8", num_workers=4)
for _ in range(3)
]
def use_fasterWhisper(model:WhisperModel=None,wav_path:str=None):
segments, info = model.transcribe(wav_path, beam_size=5, language="en",vad_filter=True)
for segment in segments:
print("[%.2fs -> %.2fs ] %s" % (segment.start, segment.end, segment.text))
return segment.text
# 用 itertools.cycle 实现轮询分配模型
model_cycle = itertools.cycle(model_pool)
async def use_fasterWhisper_async(model: WhisperModel, wav_path: BinaryIO):
# 因为transcribe是阻塞,使用线程池跑
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
result = await loop.run_in_executor(None, lambda: use_fasterWhisper(model, wav_path))
return result
@app.websocket("/ws")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
await websocket.accept()
try:
num = 0
while True:
num += 1
print(f"chunk---->[ {num} ]")
audio_chunk = await websocket.receive_bytes()
f = io.BytesIO(audio_chunk)
# 轮询选择模型
model = next(model_cycle)
# 异步调用阻塞推理
result = await use_fasterWhisper_async(model, f)
# result = num # 模拟返回结果
if result is not None:
await websocket.send_json({"text": result})
except WebSocketDisconnect:
print("Client disconnected")
def main():
uvicorn.run(app, host="127.0.0.1", port=11451)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
压测端
from locust import User, task, between, events
import websocket
import json
import time
import random
import soundfile as sf
import io
import threading
# 读取音频并切成 1 秒块
AUDIO_FILE = "sounds/0950f810192c495e9191723524097673.wav"
audio, sr = sf.read(AUDIO_FILE)
chunk_size = sr
chunks = [audio[i*chunk_size:(i+1)*chunk_size] for i in range(len(audio)//chunk_size)]
def chunk_to_bytes(chunk):
buf = io.BytesIO()
sf.write(buf, chunk, sr, format="WAV")
return buf.getvalue()
chunk_bytes_list = [chunk_to_bytes(chunk) for chunk in chunks]
class WSUser(User):
wait_time = between(0.1, 0.5) # 模拟较高请求频率
def on_start(self):
self.ws = websocket.create_connection("ws://localhost:11451/ws")
def on_stop(self):
self.ws.close()
@task
def send_audio(self):
audio_bytes = random.choice(chunk_bytes_list)
start_time = time.time()
try:
self.ws.send(audio_bytes, opcode=websocket.ABNF.OPCODE_BINARY)
resp = self.ws.recv()
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
try:
data = json.loads(resp)
text = data.get("text", "")
except Exception:
text = ""
# 成功 or 失败事件
events.request.fire(
request_type="WS",
name="send_audio",
response_time=total_time,
response_length=len(resp),
exception=None if text else Exception("Empty text")
)
except Exception as e:
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
events.request.fire(
request_type="WS",
name="send_audio",
response_time=total_time,
response_length=0,
exception=e
)
启动压测脚本
locust -f benchmark/run_loust.py --headless -u 50 -r 10 --run-time 2m --html report.html --csv=report_prefix
数据
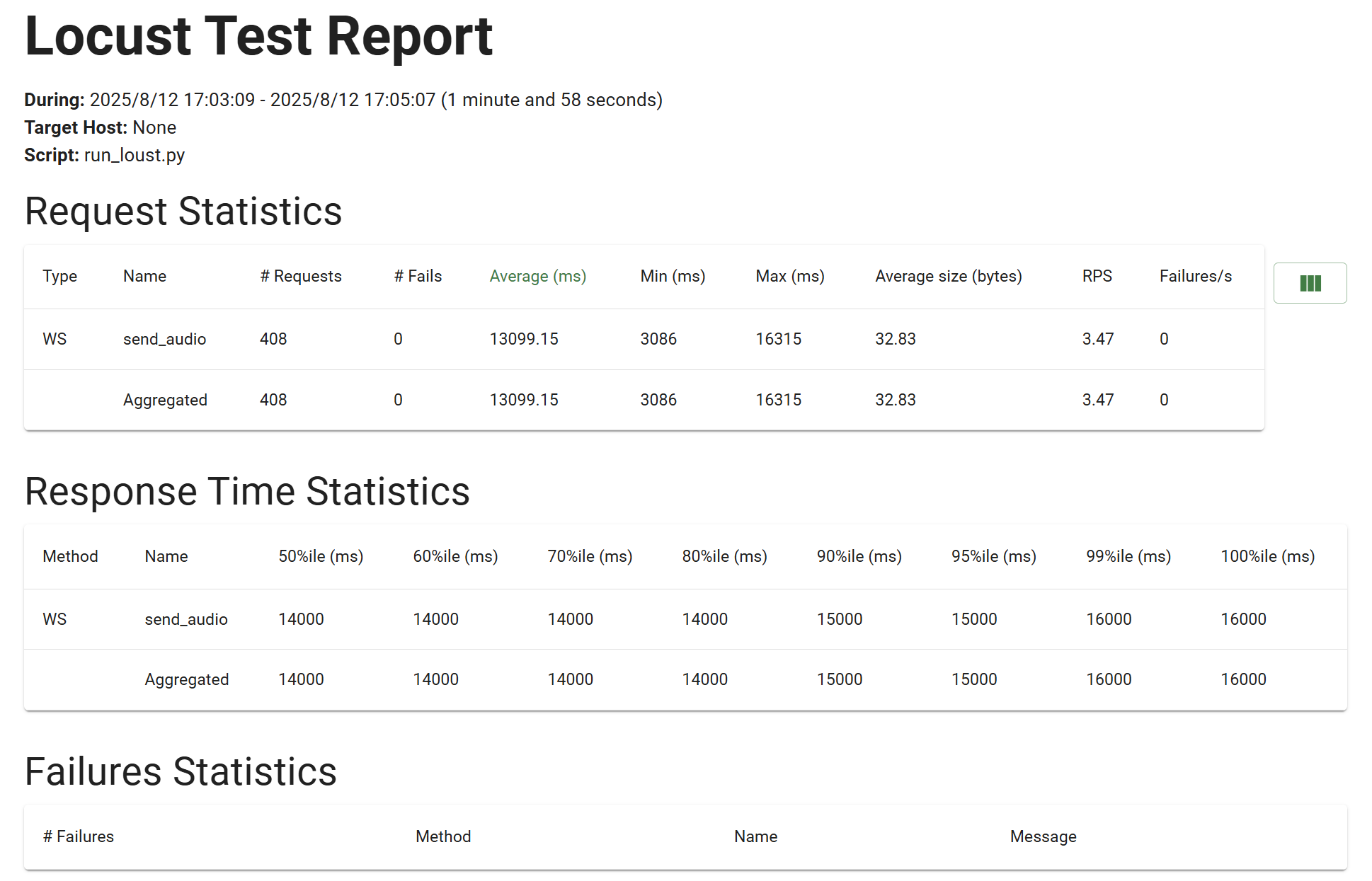
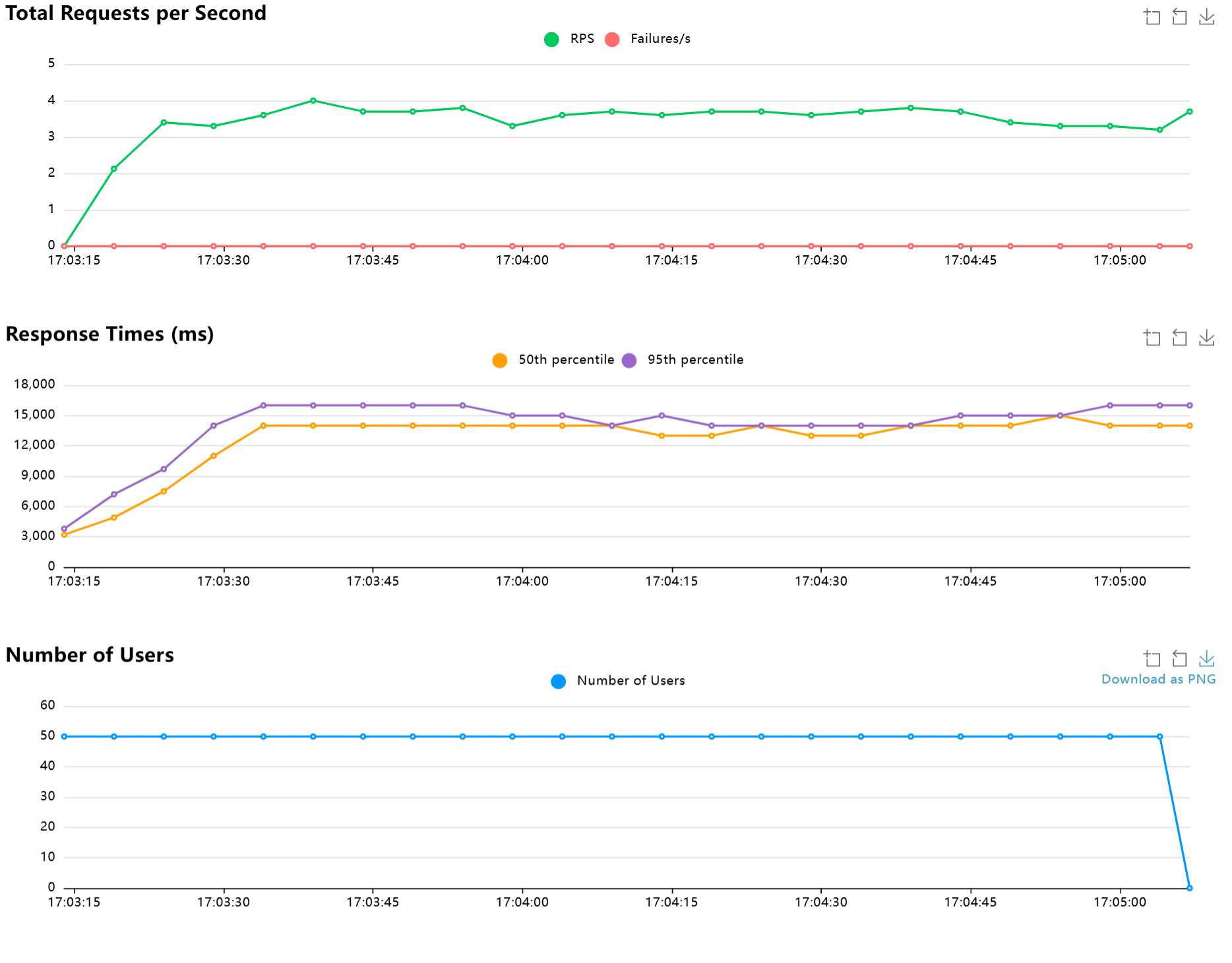
Tesla T4 16G
Final ratio
Ratio Per Class
- 100.0% WSUser
- 100.0% sendAudio
Total Ratio
- 100.0% WSUser
- 100.0% sendAudio
从上述的数据可以看出,单台tesla要保证伪实时语音识别的情况下是很困难的,单台Tesla T4大概只能支持3人左右实时使用
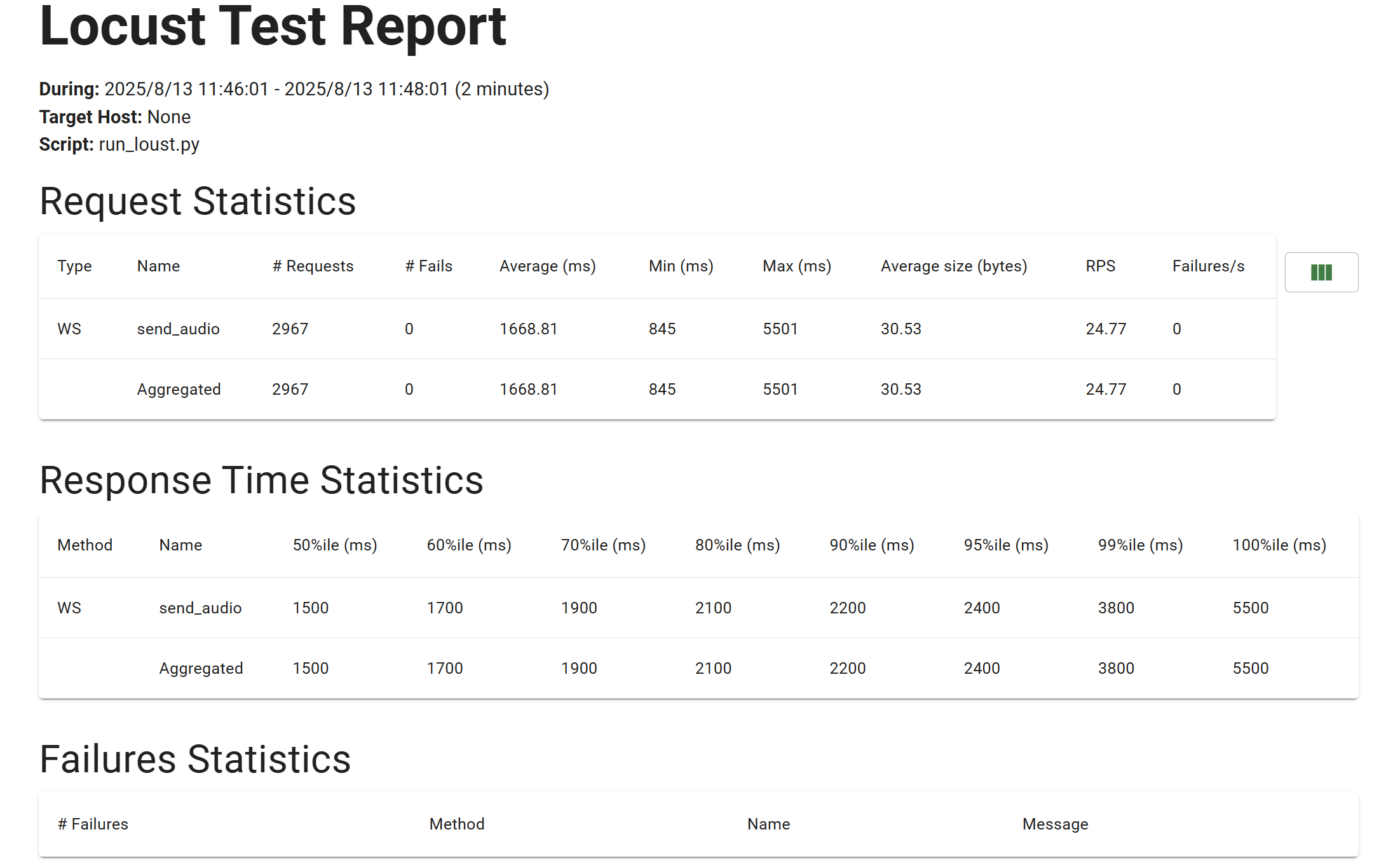
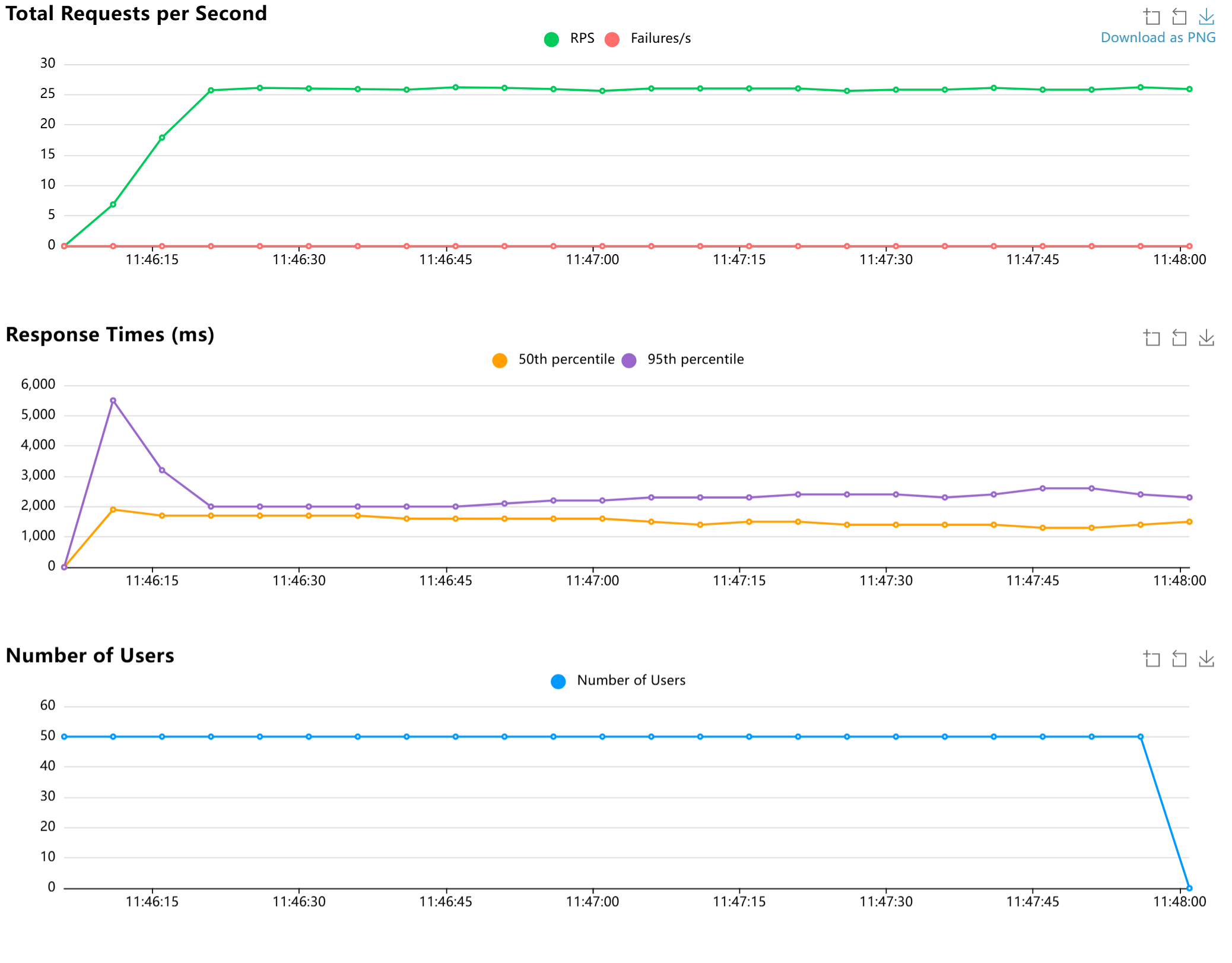
A100 80G
Final ratio
Ratio Per Class
- 100.0% WSUser
- 100.0% sendAudio
Total Ratio
- 100.0% WSUser
- 100.0% sendAudio
A100大概能支持24个并发